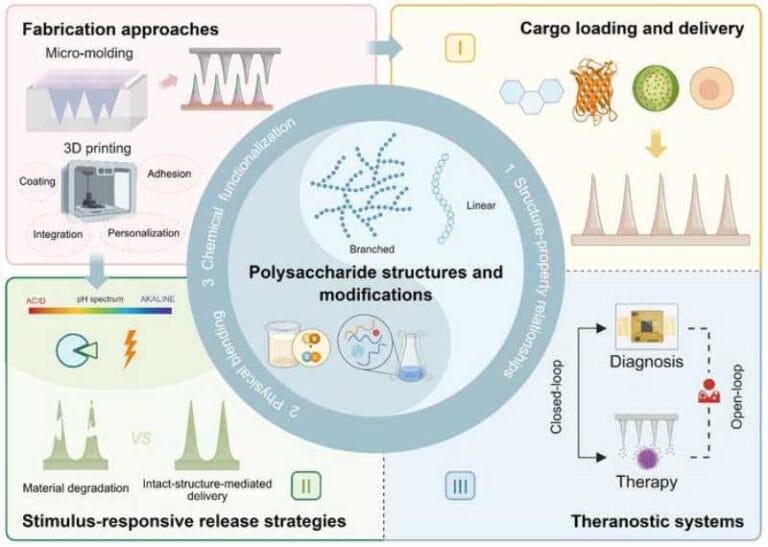
5,000-Year-Old Bacterium Found in Ice Is Resistant to Antibiotics
A team of researchers has identified an ancient bacterium frozen for approximately 5,000 years in the Scărișoara Ice Cave, Romania, exhibiting remarkable resistance to several antibiotics currently used in medicine—an observation that may…