Things on Mars that look like they shouldn’t be there

As one of the planet Earth’s most proximate celestial neighbors, Mars has long held a fascination for humans, offering the tantalizing possibility of extraterrestrial life situated merely a brief rocket journey away. Thus far, no evidence of extraterrestrial life has been discovered. However, with the advent of robotic technology, NASA and other space agencies have commenced exploration of the Martian atmosphere and surface. This has led to the discovery of a multitude of unusual features and formations, which continue to ignite a fervor of anticipation, apprehension, and curiosity among skywatchers.
The following are some of the most notable objects on Mars that appear to be incongruous on a planet that is perceived to be desolate and devoid of life. Many of these formations result from pareidolia, the tendency of humans to perceive patterns and shapes in inanimate objects. Nevertheless, some of these findings may ultimately provide scientists with the long-sought evidence of past Martian life.
An open “travel book”
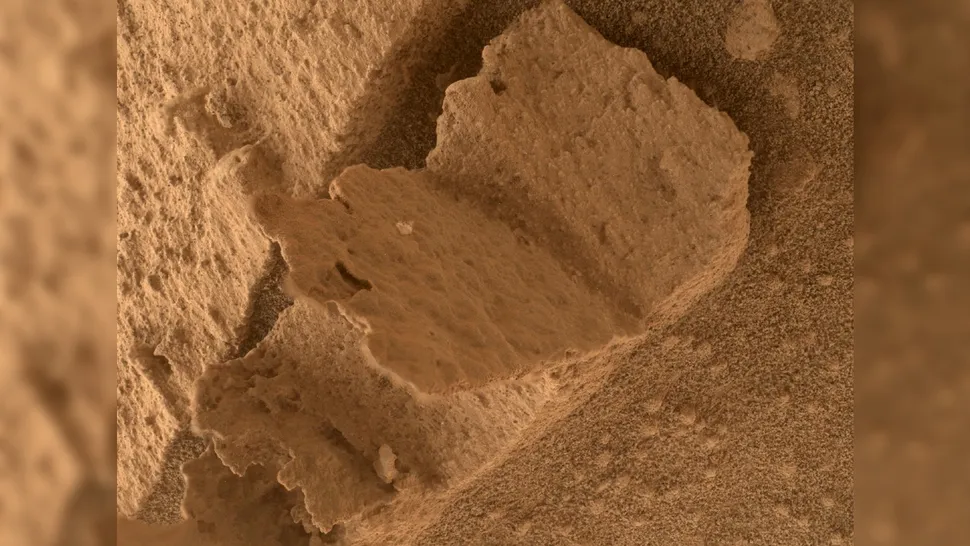

Following an exhaustive search for evidence of ancient water, NASA’s Curiosity rover paused in April 2023 to peruse an aged Martian hardback resting in the dust of Gediz Vallis. Although the peculiar object may resemble a book with a single page fixed in mid-turn, it is, in fact, merely a rock, albeit a diminutive one. The diminutive rock formation, which NASA has dubbed a “charming little book-rock,” measures a mere 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) in width. On a positive note, the object is of a sufficiently small size to be classified as travel-sized.
A “teddy bear’s face”
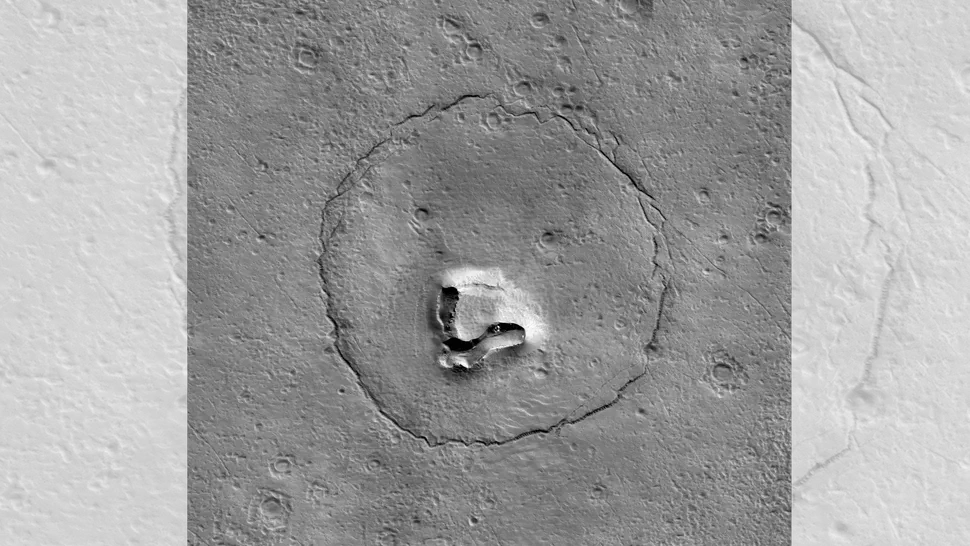
In an image disseminated by the University of Arizona (UA) in January 2023, an object that resembles an enormous Martian teddy bear is visible. This object is characterized by two beady eyes, a button nose, and an upturned mouth. It is situated in the vicinity of NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, which is equipped with a camera. According to the University of Arizona, the formation is likely the result of a collapsed hill in the center of an ancient crater. However, it can be reasonably argued that this particular formation is the most endearing pile of rubble in the known universe.
Frozen “mineral flowers”
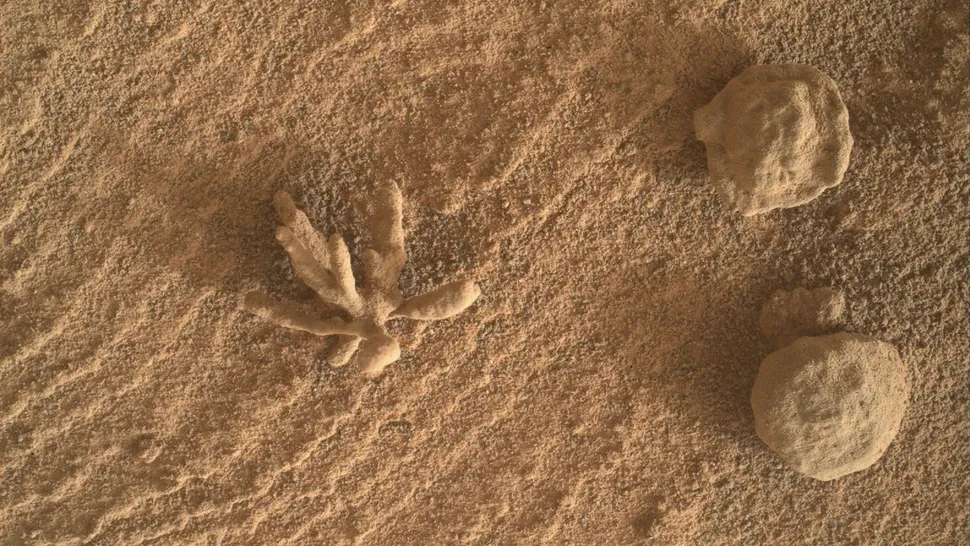

This delicate mineral flower, which resembles a tiny coral, represents the closest approximation of greenery that can be found on Mars at the present time. Mineral deposits of this nature are a common occurrence across Mars, resulting from the interaction of ancient water with ancient rock. Nevertheless, NASA researchers have noted that such a perfectly flower-like deposit is a rare occurrence. Two additional, albeit less impressive, circular rocks of the same type are visible to the right of the coral. In February 2022, the Curiosity rover observed this floral feature.
A mysterious “doorway”
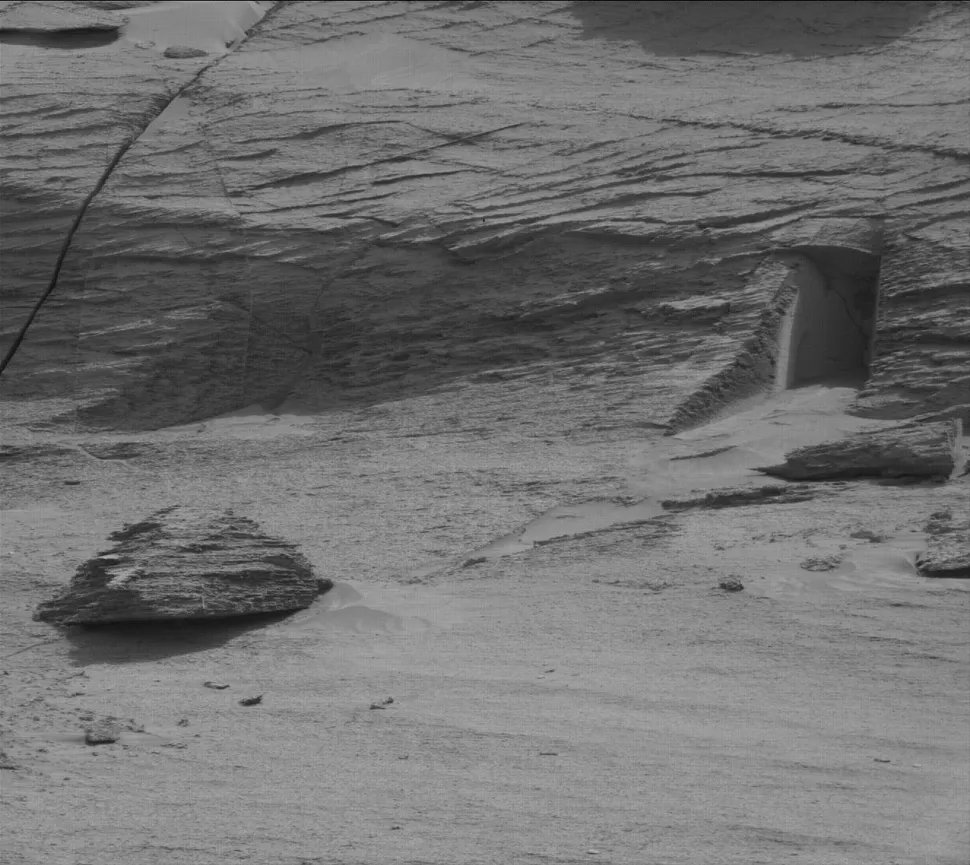

The question arises as to whether this meticulously crafted “doorway” into the Martian cliffside is evidence of intelligent extraterrestrial life on Mars or perhaps indicative of a clandestine human presence on the planet. Unfortunately for those who subscribe to the theory that this is evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence, the truth is far more straightforward: it is simply an eroded rock formation captured at the optimal angle. The image was obtained by NASA’s Curiosity rover in 2022.
Fossilized “animal tracks”
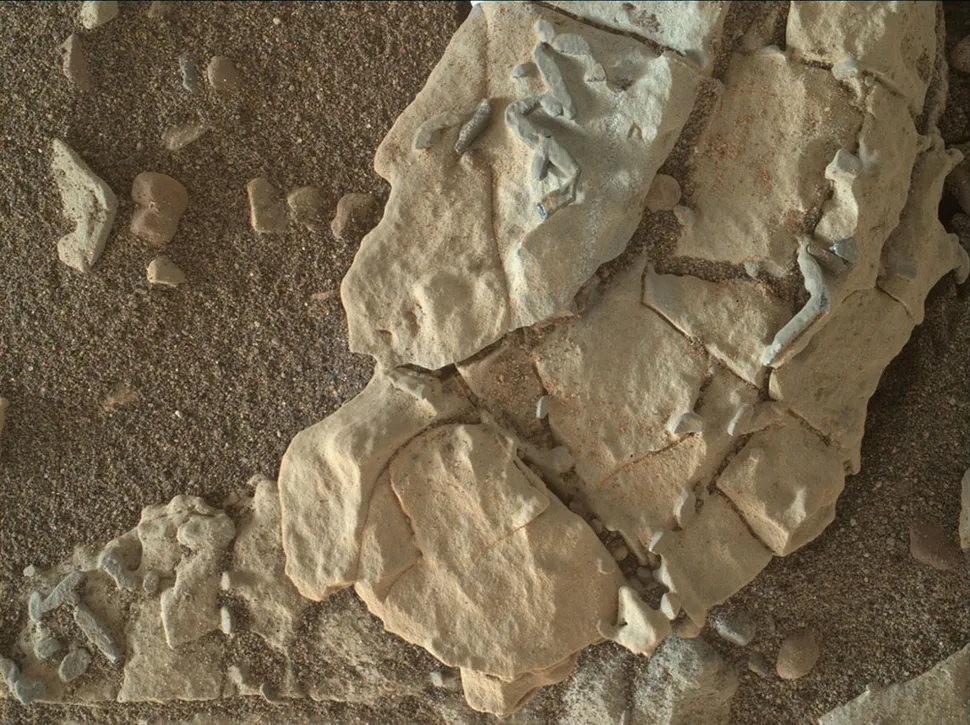

The question of whether alien creatures once traversed the surface of Mars, leaving behind fossilized traces imprinted in the geological formations, has been posed by some researchers. In 2018, one researcher advanced a controversial hypothesis, citing images of stick-like structures, each approximately the size of a grain of rice, traversing a Martian rock. NASA researchers promptly refuted the claims, noting that analogous features are prevalent on Earth in regions where salts are concentrated in water, such as evaporating lakes. The discovery of these structures on Mars provides further evidence of the existence of rivers and lakes on the planet, but it does not offer proof that life forms were ever present on its surface.
A bushel of “blueberries”
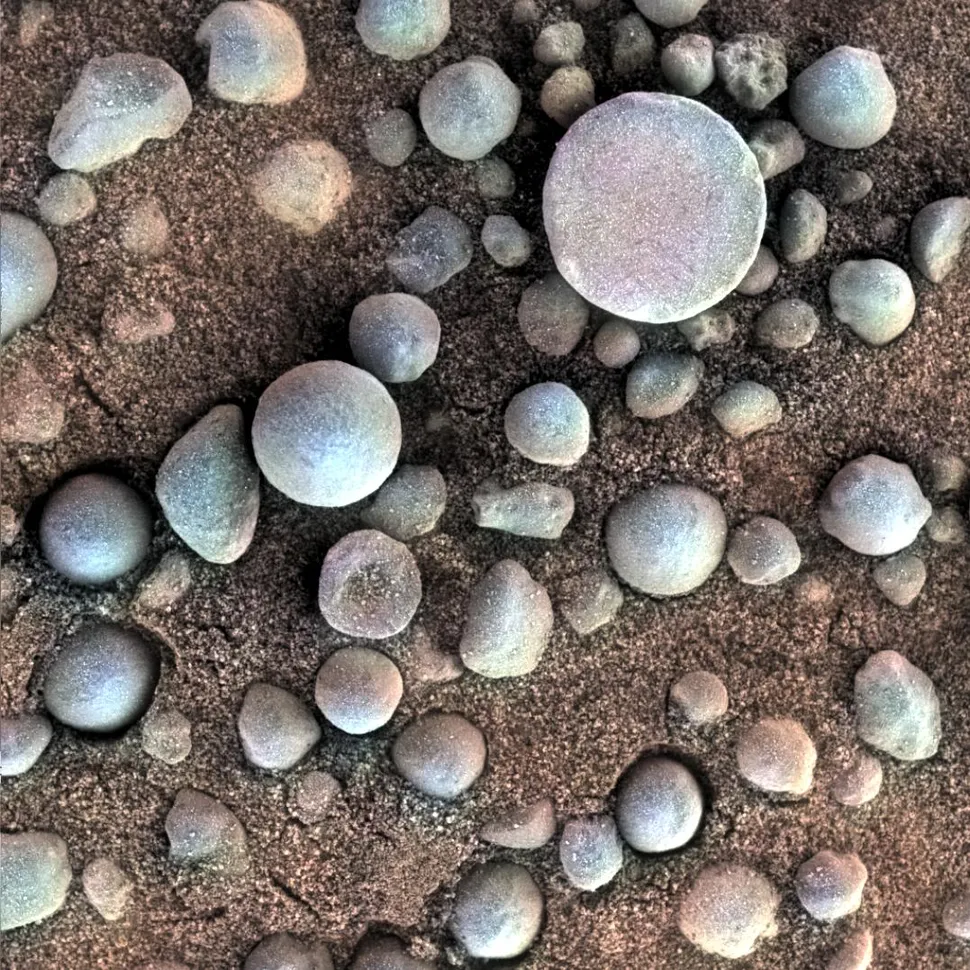

While blueberries are not a significant source of iron when consumed on Earth, the geological formations discovered by NASA’s Opportunity rover on Mars in 2004, which have been dubbed “blueberries” by scientists, are built differently. The iron-rich spheres, which have been polished smooth by plentiful amounts of water over the course of billions of years, represent some of the earliest evidence that scientists have of Mars having once been an incredibly wet world. The potential for these spheres to enhance the flavor of cheesecake remains an open question for future research.
Thousands of black “spiders on Mars”
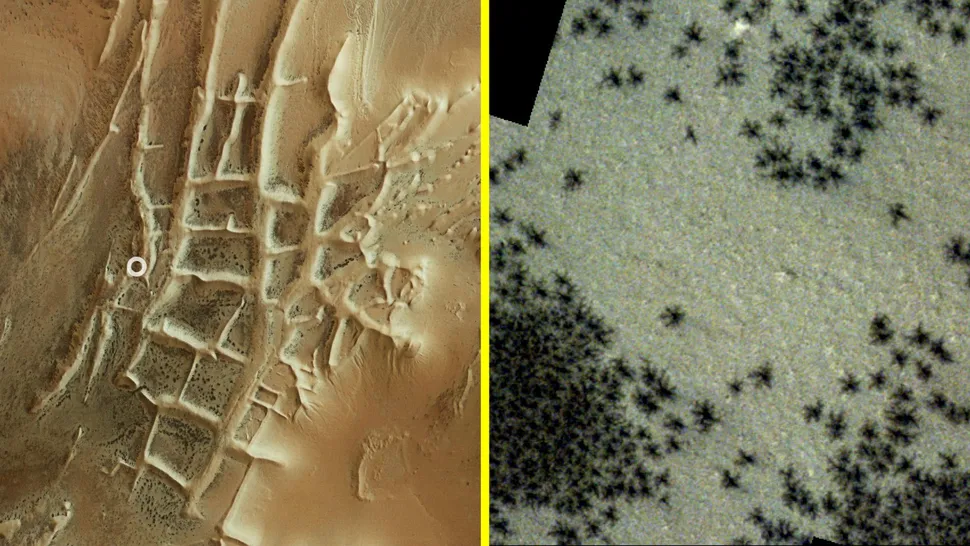
Each spring, thousands of squiggly black entities emerge from their hibernation near the Martian south pole. These entities have been identified as squiggly black “spiders.” It is important to note that these structures are not, in fact, spiders. They are not alive, and they are not composed of the same materials as living organisms. The seasonal phenomenon can be attributed to the sublimation of buried carbon dioxide ice, which occurs as the weather warms and the ice transforms into a gas.
The newly released gas bursts through layers of surface ice, carrying with it dark dust that splatters across the ground in craggy patterns. In order for these formations to be visible from space, the “spiders” must be relatively large. Each one is estimated to measure between 150 and 3,300 feet (45 meters to 1 kilometer) across, according to the European Space Agency (ESA). It would be prudent to refrain from disclosing this information to Ziggy Stardust.
Ruins of an “Inca City”
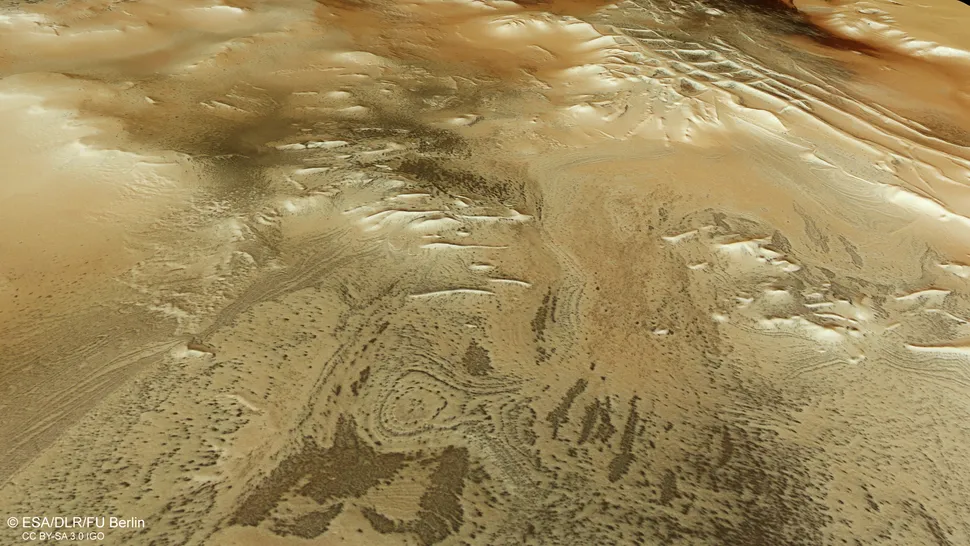
In the vicinity of the Martian south pole, there are structures that bear a striking resemblance to the ruins of a vast and ancient city. The formation has been designated the “Inca City” due to its resemblance to actual ruins discovered in South America. However, the ESA has proposed an alternative hypothesis, suggesting that the formation may be composed of elevated sand dunes that have undergone a process of petrification over time.
Nevertheless, the precise origin of this formation remains uncertain. The labyrinthine formation appears to curve, forming part of a giant circle 53 miles (86 km) in diameter. This leads scientists to hypothesize that it may be part of a much larger impact crater from a meteor strike that occurred in the distant past.
An ancient smiley face
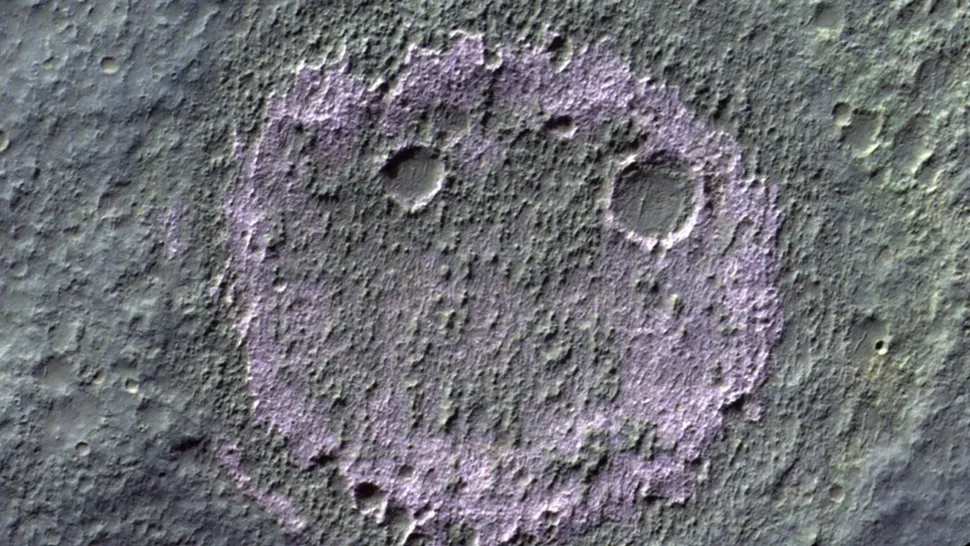
It would appear that an image of a grinning face has been painted onto the Martian surface. This is not the case, despite the visual impression conveyed by this infrared image captured by the ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter. The face-like structure is visible only under certain conditions. It is, in fact, the remnants of an ancient lake, outlined by chloride salt deposits and dotted with two meteor crater eyes.
While it is unlikely that any Martian graffiti artists will emerge from the lake to claim credit for their work, the face-like structure may contain evidence of ancient life on Mars. As Mars’ formerly abundant lakes evaporated, the remaining water sources are likely to have become highly saline, potentially providing a habitat for microbial life.
An extremely out-of-place rock
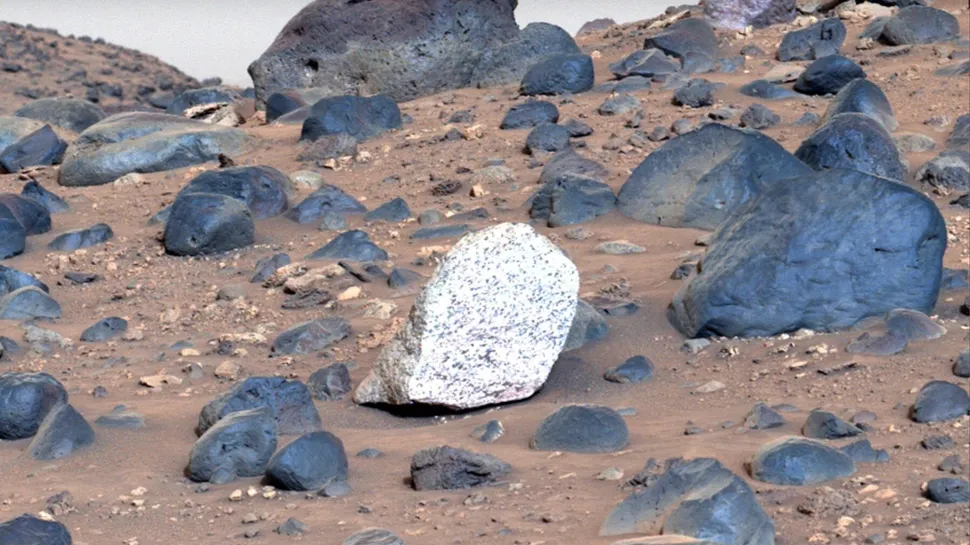

This unusually white rock, which stands out starkly against the dusty backdrop of Jezero Crater, represents a previously unobserved phenomenon on Mars. The rock, dubbed “Atoko Point” after a similarly light-colored feature of the Grand Canyon, is believed to be composed of minerals such as pyroxene and feldspar, according to an analysis conducted by NASA’s Perseverance rover.
The question thus arises as to how such a white rock came to be situated in such a dark-hued environment. It is probable that the rock fell from the crater rim or was transported to the crater floor from another location on Mars at a time when rivers were present in the region.
A stony “Star Trek” symbol
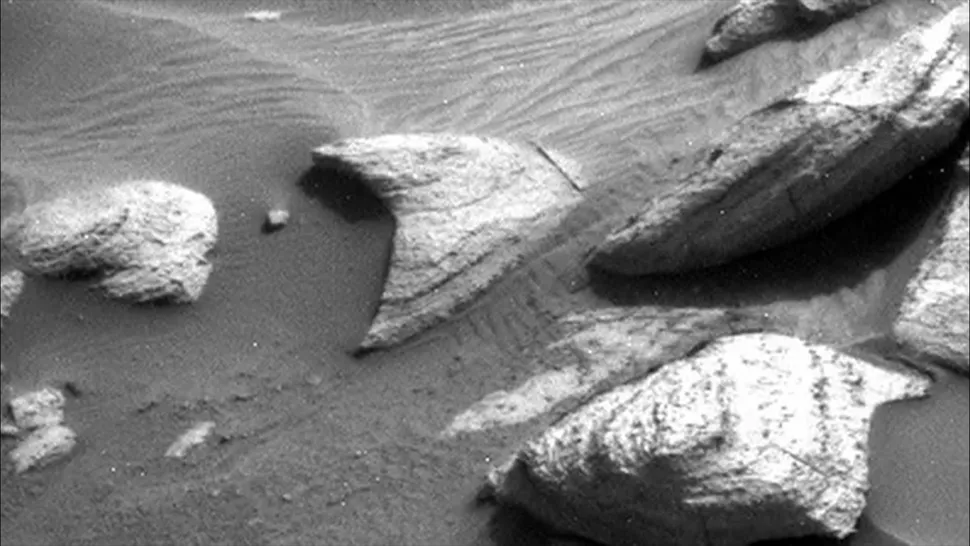

It appears that a Starfleet communicator badge may have been left behind on Mars, as evidenced by the distinctive shape of a rock observed by the Curiosity rover. NASA has stated that the rock’s delta shape is merely a coincidence. It is one of thousands of similar rocks located on Mount Sharp, which the Curiosity rover has been exploring for years in its search to uncover clues about Mars’ past and whether it ever held the conditions for life.
A “tile floor”
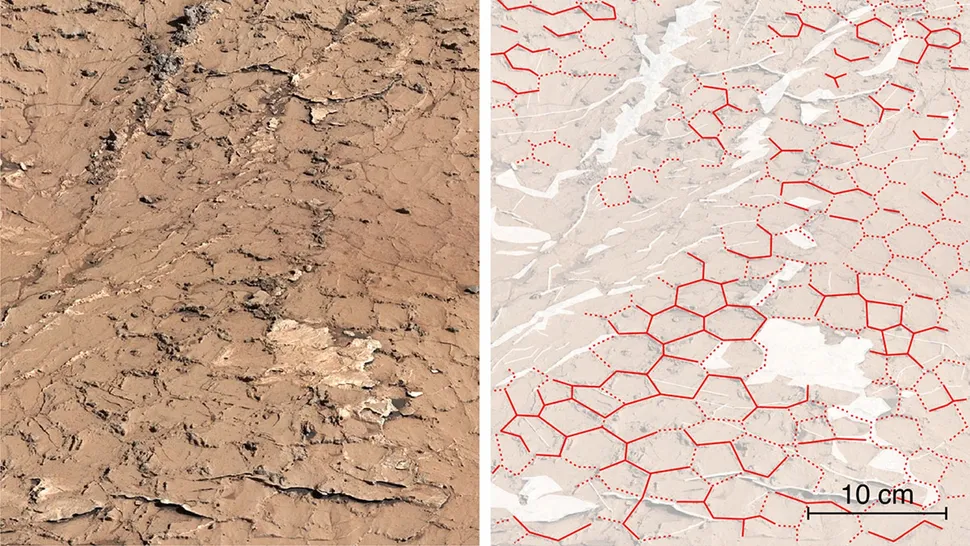

During its 2021 excursion up Mount Sharp, NASA’s Curiosity rover discovered what appears to be the remnants of a tile floor, indicative of a Martian bathroom. Dozens of interlocked polygons were observed to have cracked through the soil; the majority of these polygons contain five or six sides and are estimated to date to between 3.8 billion and 3.6 billion years ago.
These jagged polygons are mud cracks, which have undergone repeated cycles of desiccation and rehydration over the course of an undetermined span of time. It is probable that these polygonal cracks in the ground date from a period when the water level in the surrounding Gale Crater fluctuated repeatedly, causing the cracks to appear and disappear over time before a final dry spell left them as they are today.
Perfectly circular sand dunes
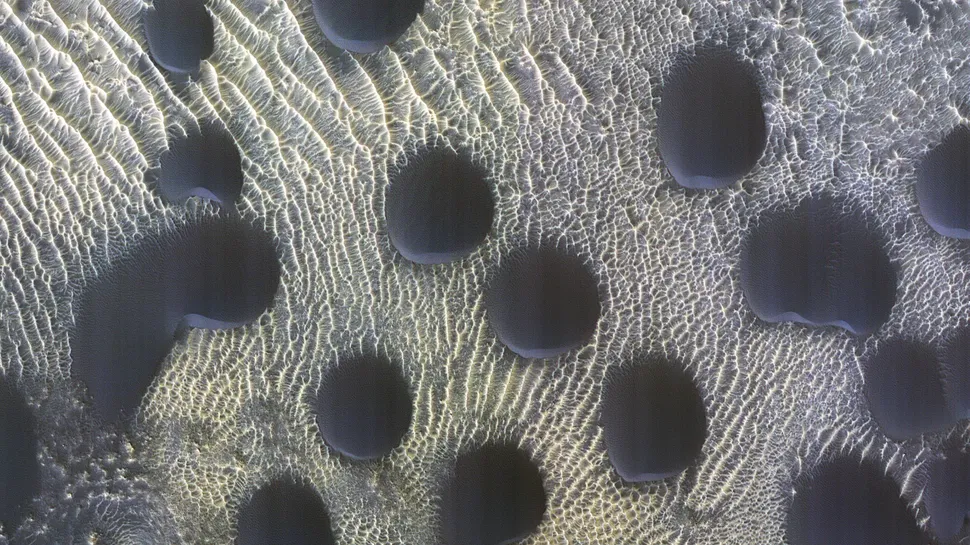
Mars is covered in a vast array of dunes, exhibiting a diverse range of shapes and sizes. However, few of them are as perfectly circular as the group observed by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2022. The image, captured while the spacecraft was traversing the northern hemisphere of Mars, depicts a heterogeneous assemblage of dark, anomalous, and circular dunes, oriented southward in a manner consistent with the prevailing winds on the planet.
The precise reason for the circular shape of these dunes and the observed migration away from the Martian equator at a rate of approximately 3.3 feet (1 m) per Martian year (equivalent to 687 days on Earth) remains unclear.
A “shark fin” and a “crab claw”
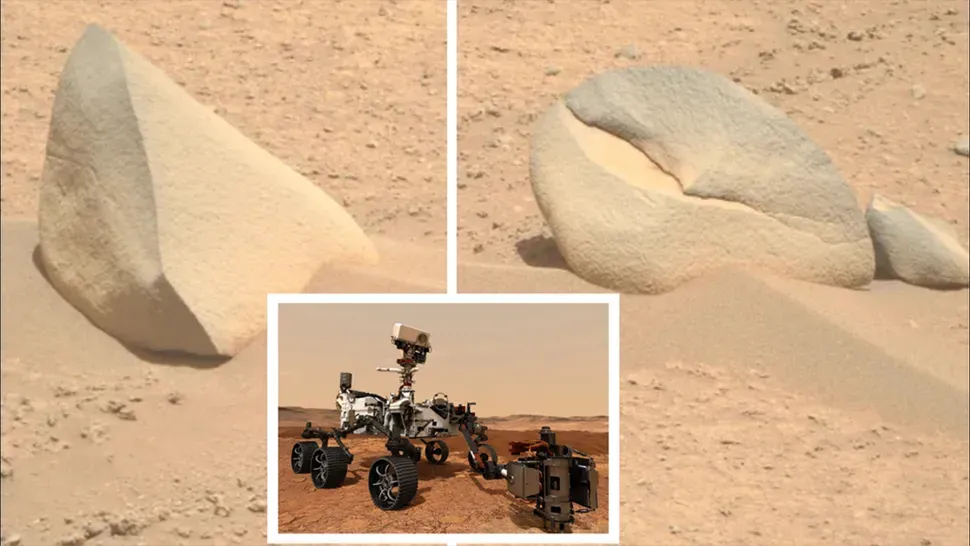

While traversing Jezero Crater, NASA’s Perseverance rover observed several geological formations that bore a resemblance to fish. The two anomalous boulders, one exhibiting an upward projection akin to a shark fin and the other displaying a crimped morphology reminiscent of a crab claw, elicited a pronounced response from the research team.
Nevertheless, the nature of these formations is relatively straightforward. They are simply rocks that have been shaped by wind erosion over a period of billions of years and left in the Martian dust for human minds to discern patterns within.
A “floating spoon”
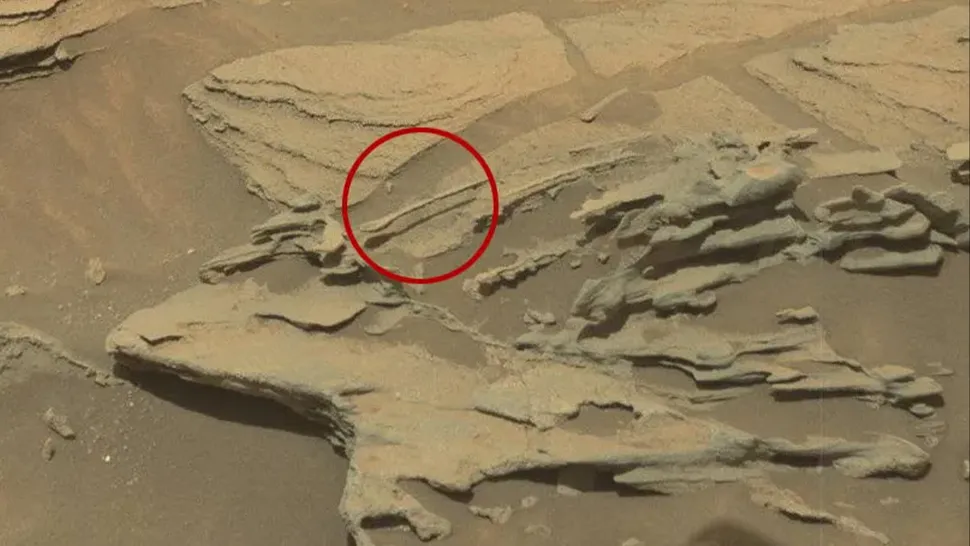

In 2015, the Curiosity rover, operated by NASA, observed an object that seemed to be a wooden spoon suspended in midair, with a shadow cast on the ground beneath it. It was, of course, an optical illusion; the spoon is simply a rock that has been shaped by the wind over a long period of time, also known as a ventifact. The handle of the spoon-shaped rock extends from a larger geological formation, enabling the rounded tip to remain suspended above the ground, creating a discernible shadow beneath it.
An eerie “face”

One of the earliest Martian rock formations to capture the public’s interest was this infamous “face,” which was first observed by NASA’s Viking 1 satellite in 1976. While surveying the planet in search of a suitable landing site for its robotic companion, Viking 2, the satellite observed a mound of rocks, partially obscured by shadow, which bore a striking resemblance to a human face.
Subsequent observations with subsequent spacecraft demonstrated that the face was discernible only from specific angles and under specific lighting conditions, thereby substantiating the hypothesis that the Martian mound’s humanlike appearance was merely an optical illusion.
A “giant’s fingerprint”
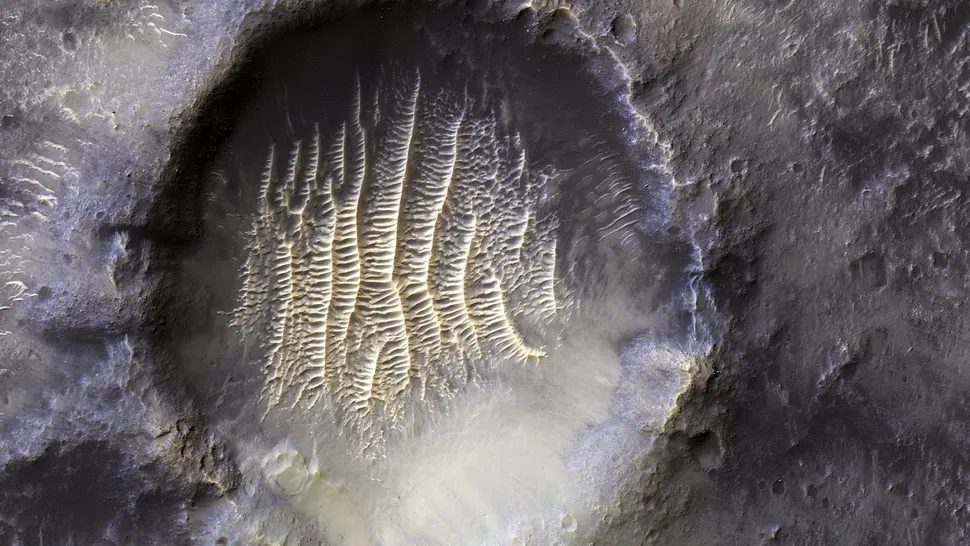

A significant impact event occurred on Mars at some point in the distant past, resulting in the formation of a massive, ridge-filled depression that bears a striking resemblance to a thumbprint. It would be erroneous, however, to conclude that a giant finger was the culprit. Situated within a considerably larger crater designated Airy-0, this Martian formation can be attributed to an ancient meteor impact.
The bright striations that form the “lines” of the fingerprint are a common feature observed across Mars. These formations are referred to as transverse aeolian ridges and are formed when sand dunes are coated in a thin layer of dust. The presence of reflective minerals within the dust is likely responsible for the observed glow in this image.
An “angel” and a heart
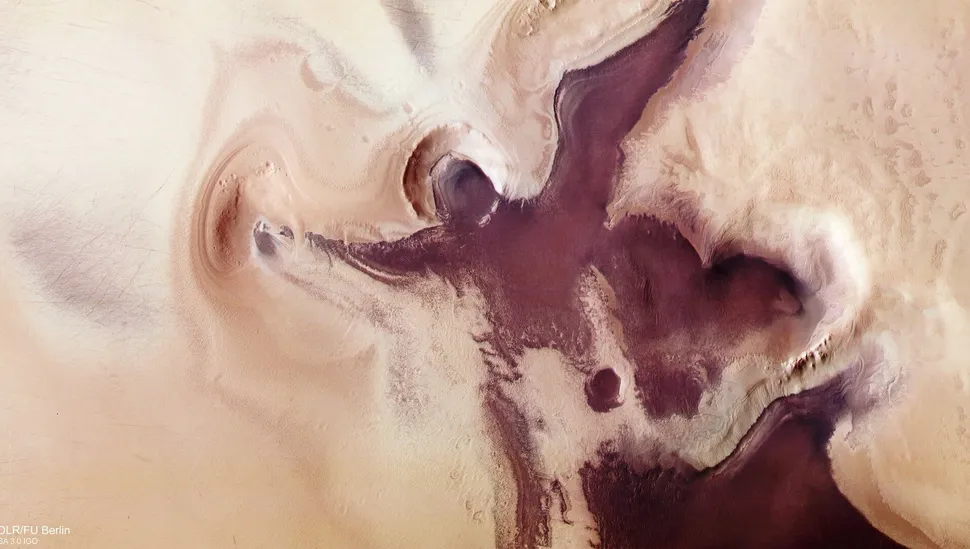

During the Martian summer, the planet’s surface is transformed into a playground for celestial bodies. The Martian south pole is typically shrouded in an expansive ice cap; however, when the ice melts in warmer conditions, patterns emerge in the ancient, red-hued sediment below. The image, captured by the ESA’s Mars Express spacecraft, depicts an angel-like pattern juxtaposed against a heart-shaped one. The formation of both these structures can be attributed to the impact of meteors, which excavated the Martian surface, exposing the underlying, darker sedimentary deposits.
A weirdly green rock with “drill holes”
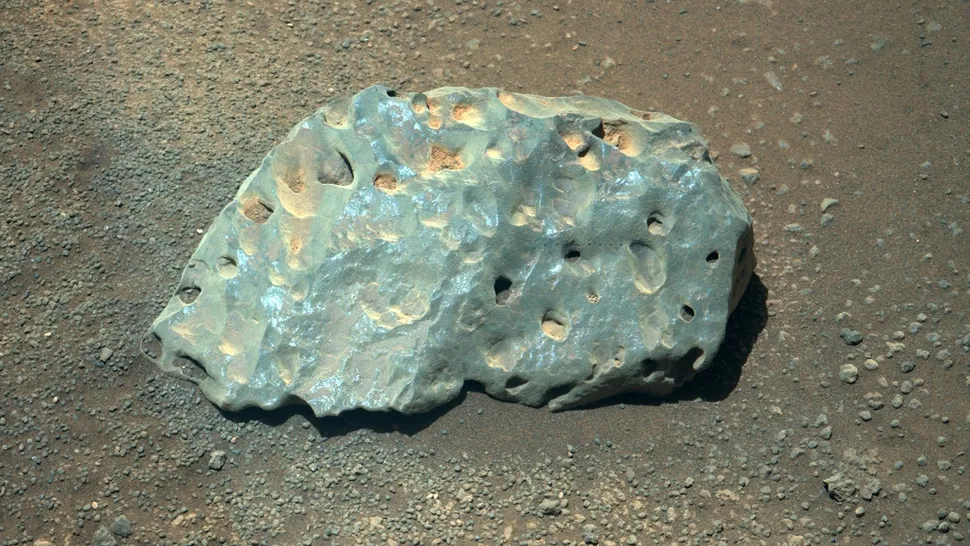

Has an adolescent Martian once again misappropriated his parents’ power tools? This is one possible explanation for the observation of a peculiar, green rock, seemingly filled with drill holes, which was documented by NASA’s Perseverance rover at the outset of its mission. The approximately 6-inch (15 cm) rock appears anomalous within its context, and the scientific community is yet to formulate a comprehensive explanation for its presence.
It is possible that the rock is the remnant of a meteor that collided with Mars, or perhaps it is a piece of Martian bedrock that was flung far across the planet during an impact event. The majority of the holes remain enigmatic. However, upon closer examination, a series of minute, uniform pockmarks, created by the laser aboard Perseverance, can be discerned. These were fired at the rock in an effort to ascertain its composition.
A small “foreign object”
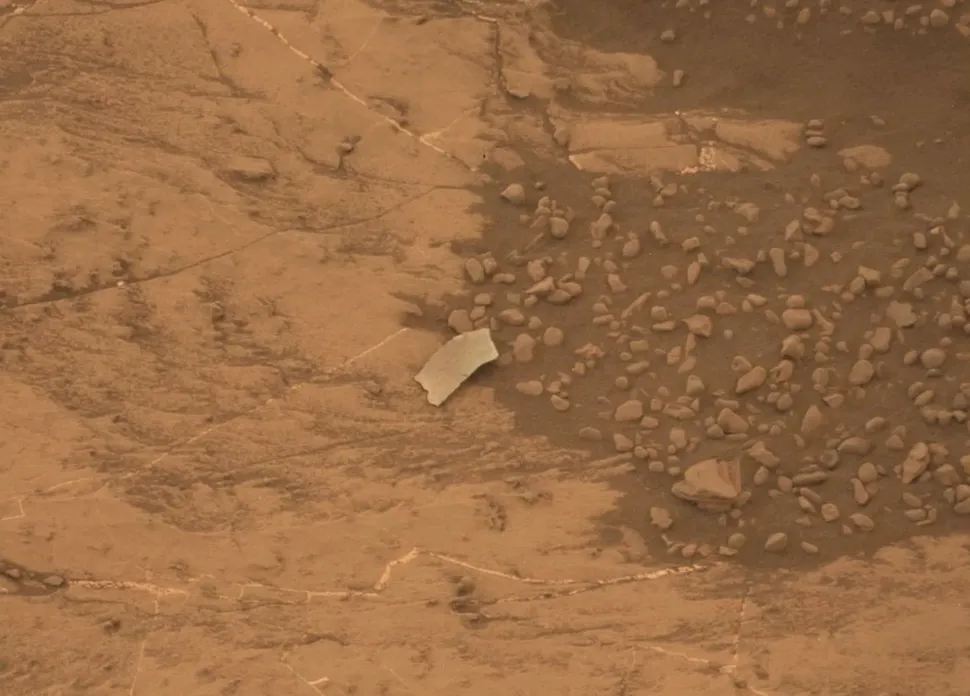

In 2018, a small, rectangular object was observed in the Gale Crater on Mars. This prompted concern among NASA scientists, who initially believed it to be a potentially hazardous object. The object bore a resemblance to a dusty sheet of metal, prompting speculation that it might be a chunk of the Curiosity rover that had fallen off. Fortunately, a prompt examination revealed that the “foreign object,” as initially designated by NASA, was merely a fracture of rock detached from a larger formation and not an extrinsic element of Gale Crater.
A strange, white tower
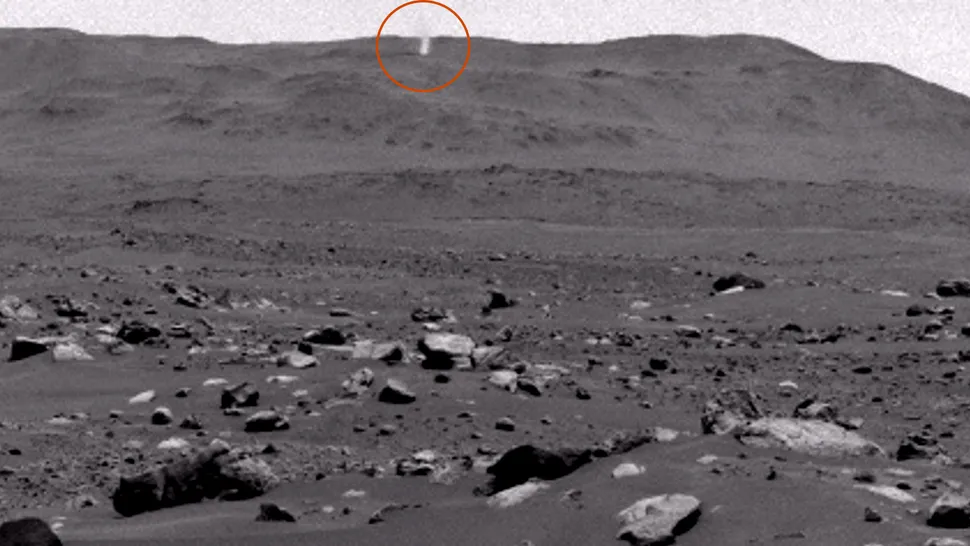

In an image captured by NASA’s Perseverance rover in 2023, a tall, white column is observed to stand against the dark, rocky background of the Martian horizon. It is, in fact, a Martian dust devil. Furthermore, the dust devil is of considerable magnitude. The dusty vortex captured in this image is taller than an average tornado on Earth and approximately five times taller than the Empire State Building, according to data provided by NASA. Dust devils are formed when rising cells of warm air meet falling columns of cool air. They are exceedingly common on Mars, with an estimated 145 million per day, according to a 2018 study.
A “scar” longer than the Grand Canyon
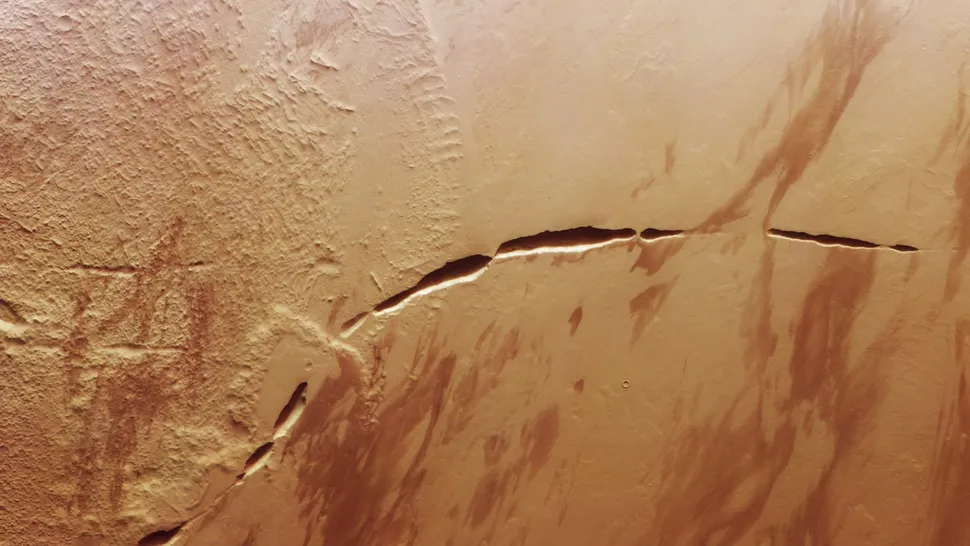

The Martian feature known as Aganippe Fossa, as observed by the ESA’s Mars Express orbiter in 2024, presents a striking image. The gaping formation is a notable feature within the Martian landscape. The extensive, profound ravine spans approximately 375 miles (600 km), a length that exceeds that of the Grand Canyon, which measures approximately 277 miles (446 km).
The Martian canyon is situated in close proximity to the base of an extinct volcano. It is postulated that the canyon was formed as a consequence of ancient volcanic activity, potentially involving the eruption of a substantial magma reservoir beneath the volcano, which exerted a powerful upward force, resulting in the fracturing of the surrounding terrain. This hypothesis has been put forth by the ESA.
“Rock candy,” or ultra-rare crystals?
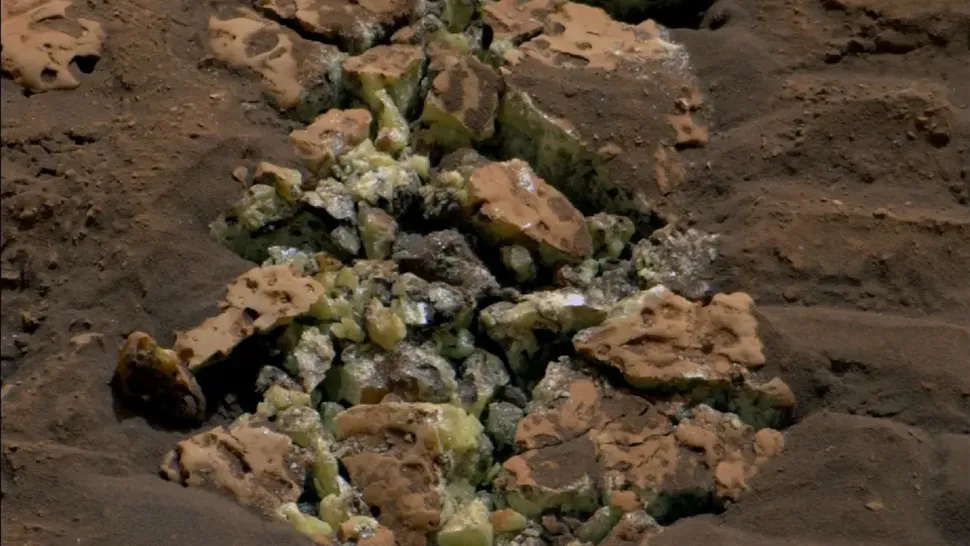

The anomalous colored crystals on Mars were fortuitously identified. In May 2024, the Curiosity rover, operated by NASA, inadvertently crushed a small rock while traversing its route. A collection of rare minerals, including some previously unseen on Mars, was unearthed from the stone tomb. The yellowish crystals are composed of pure elemental sulfur. Scientists had long anticipated the existence of this material on Mars but lacked definitive proof until the destructive driving incident involving Curiosity.
A “bullet” hole
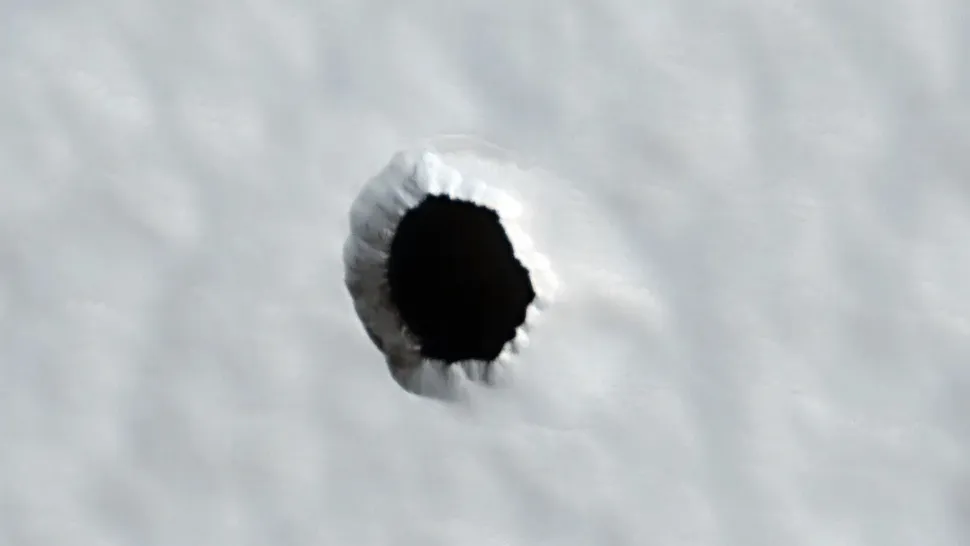

The formation observed in the Martian landscape, which bears resemblance to a bullet impact, may in fact represent a promising potential refuge for future astronauts. The hole, which measures a few meters across, was imaged by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2022 on the flank of a massive volcano called Arsia Mons. The pit is situated along a lava flow and appears to be a vertical shaft that may potentially connect to a deep system of caverns situated below the volcano. While the depth of the hole remains unknown, it may prove an appealing refuge for future astronauts seeking protection from the considerable radiation levels present on Mars.
An underground “dog”
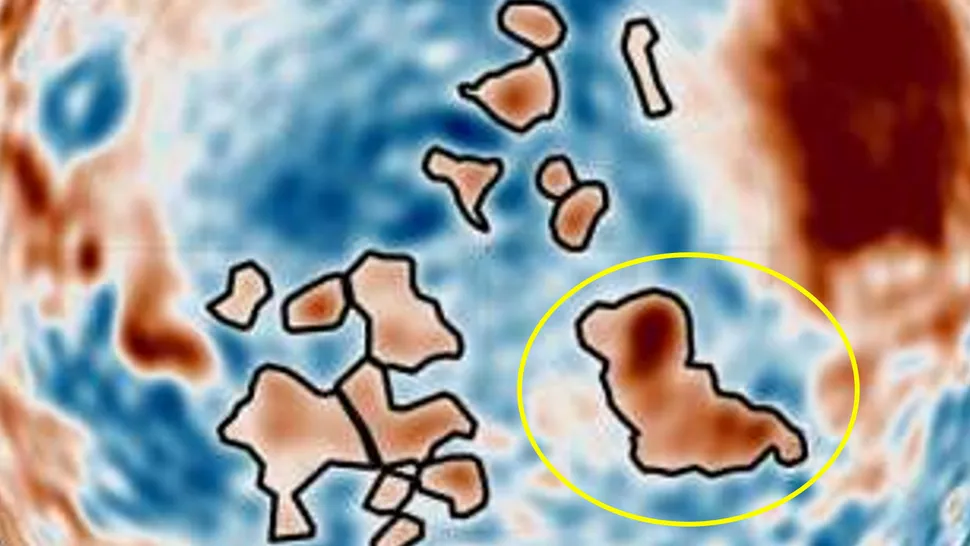
The presence of anomalous structures is not exclusive to the Martian surface; they also manifest within the planet’s subterranean environment. In September 2024, researchers synthesized data from multiple Mars-orbiting spacecraft to construct a comprehensive map of gravitational anomalies—areas where the gravitational pull is stronger than average, indicating the potential presence of massive, dense structures beneath the planet’s surface.
The majority of these dense blobs are amorphous, yet one in particular captured the researchers’ attention: a peculiar, dog-shaped structure with a dark tail and ears, situated in close proximity to the Martian north pole. The precise formation mechanism of the dense, dog-like structure remains uncertain. Potential hypotheses include a past meteor impact or a concentration of volcanic material.
Debris from outer space?
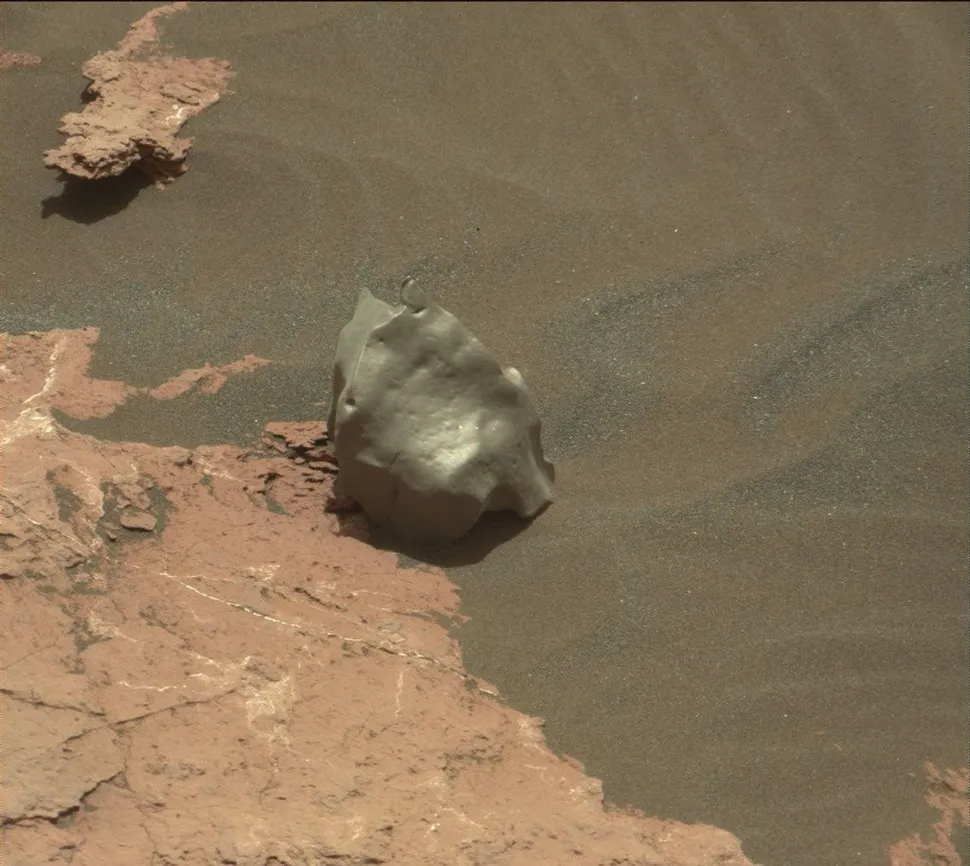

In the Gale Crater region of Mars, a NASA Curiosity rover team observed a peculiar object amidst the surrounding red rock formations. The object, a jagged gray mass, immediately captured the attention of the researchers, prompting further investigation. The shrapnel-like rock appears anomalous, and according to researchers, this is likely due to its status as a meteorite remnant. The pointy boulder is probably the result of a meteorite that crash-landed on Mars’ surface a considerable length of time ago.
The meteorite, which has been designated Ames Knob, exhibits dimensions of approximately 4 inches in width and 5.5 inches in length (10 by 14 cm). Rather than representing mere detritus from space, the rock has been identified by NASA researchers as a potential source of insights into the past conditions on Mars. These include the circumstances of the meteorite’s descent, such as whether it landed on land or in a now-vanished body of water.
Debris … from Earth?
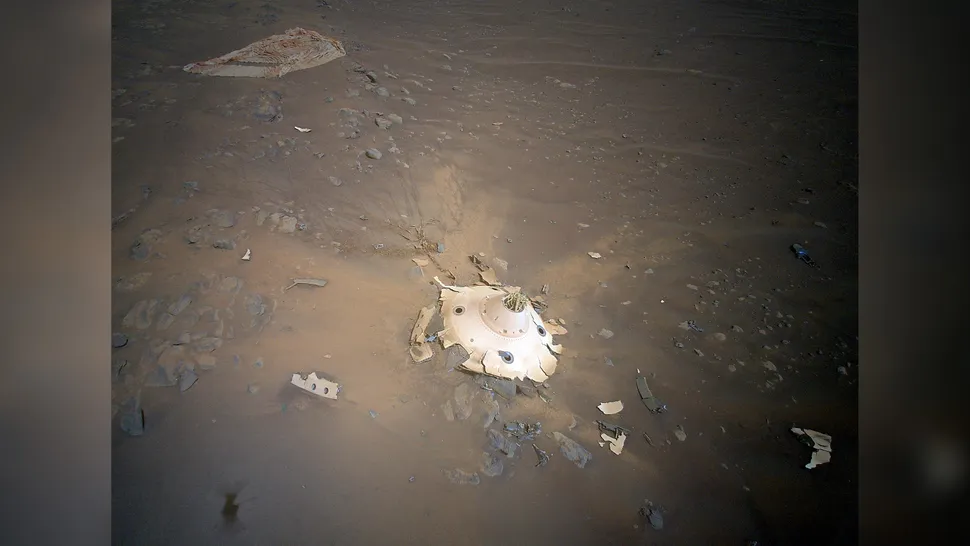

In 2022, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) observed what appeared to be the wreckage of an extraterrestrial spacecraft on the planet Mars. In this instance, the “aliens” were, in fact, terrestrial beings. The wreckage observed by NASA’s Ingenuity Mars helicopter was a section of the helicopter’s parachute and backshell, a disc-like covering that assisted in decelerating the robotic craft’s descent as it descended onto the planet along with the larger Perseverance rover.
This piece of wrecked human technology, photographed by Ingenuity while it was flying at an altitude of 26 feet (8 meters) above the Martian surface, appears particularly alien when viewed in the context of the surrounding landscape, which is characterized by desolate rocks and dust.
An alien “egg”?
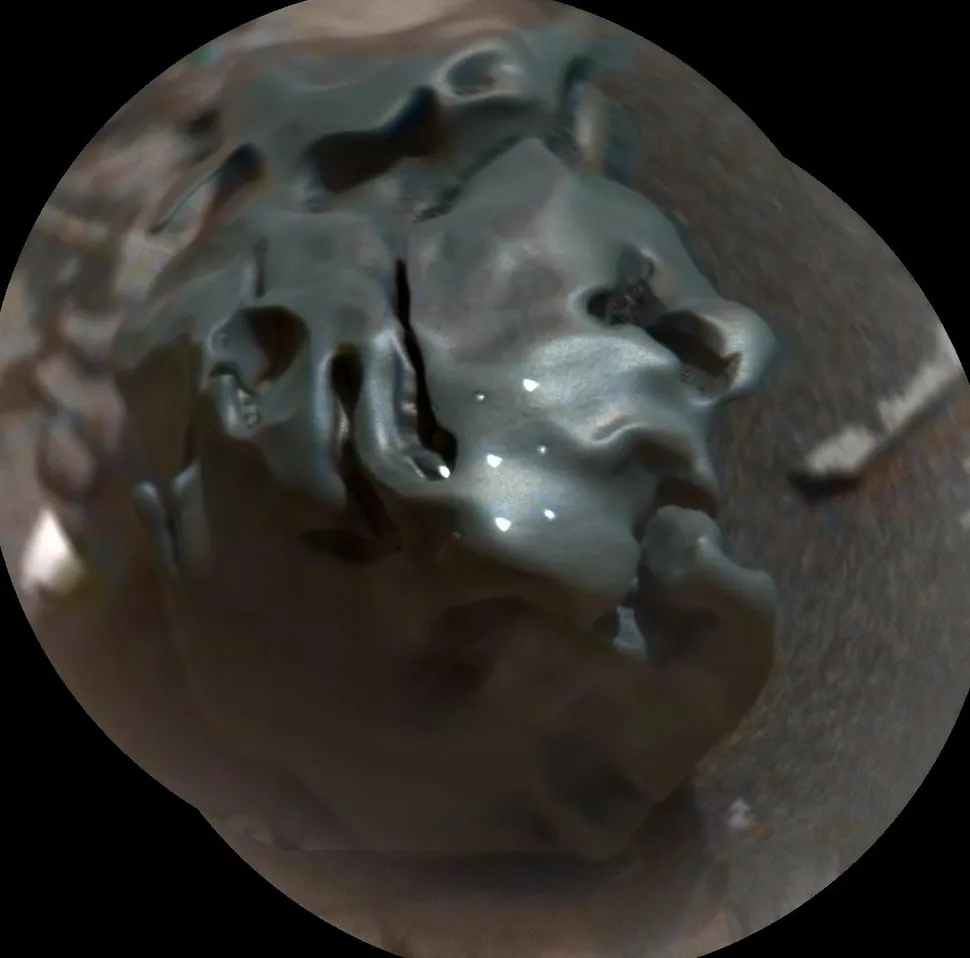
From specific perspectives, this cratered rock resembles a slimy, green egg from an unidentified alien creature. However, NASA’s Curiosity rover quickly determined through analysis that this unusual boulder, named Egg Rock, is in fact a piece of meteorite that impacted Mars at an unknown point in history. While examining meteorites on the Martian surface can provide insightful information about the planet’s history, it is improbable that such discoveries will trace back to any extraterrestrial monster origins.
Swirling patterns
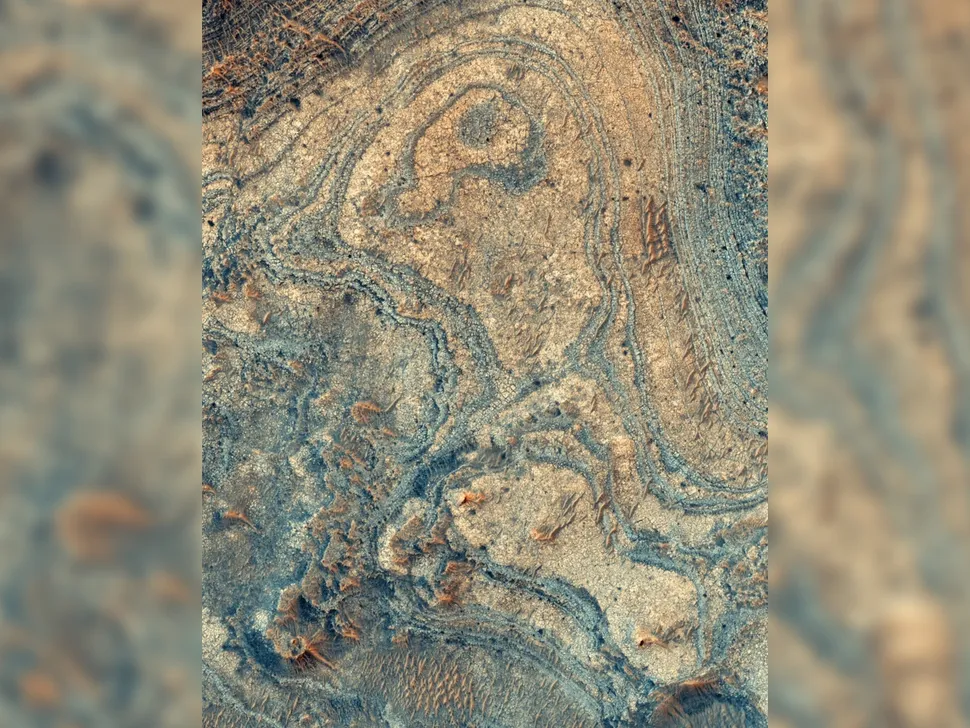

Unusual formations etched into the surface of Mars’ Nili Fossae region are neither alien creations nor the Martian equivalent of Peru’s Nazca Lines. Instead, these patterns consist of mineral deposits rich in olivine, a substance generally found deep beneath Mars’ surface. The question of how such vast amounts of olivine-rich rock reached the planet’s exterior remains an intriguing puzzle for scientists. One hypothesis suggests that a significant asteroid impact may have exposed the Martian interior, scattering olivine onto the surface. Alternatively, it is possible that volcanic activity brought the subsurface mineral to light. The exact mechanism behind its emergence, however, remains unresolved.
An alien monolith?
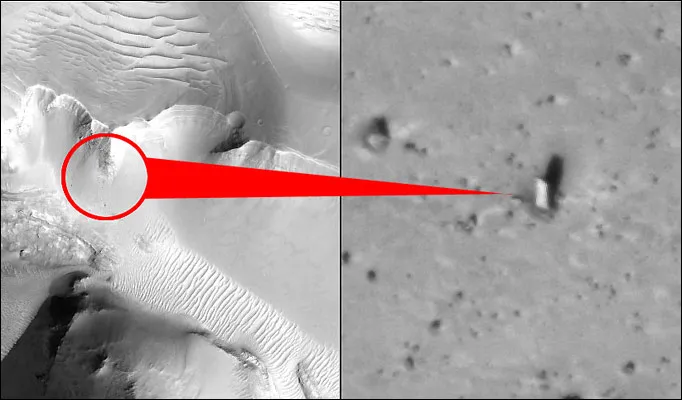
While examining images captured by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, amateur astronomers noticed an unusual feature in the satellite’s data: a strikingly rectangular object that evokes the iconic alien monolith from the opening scene of 2001: A Space Odyssey. According to mission scientists, the perplexing structure does exhibit a monolithic shape and size. However, it is most likely just a large, naturally rectangular rock.
A crawling robot
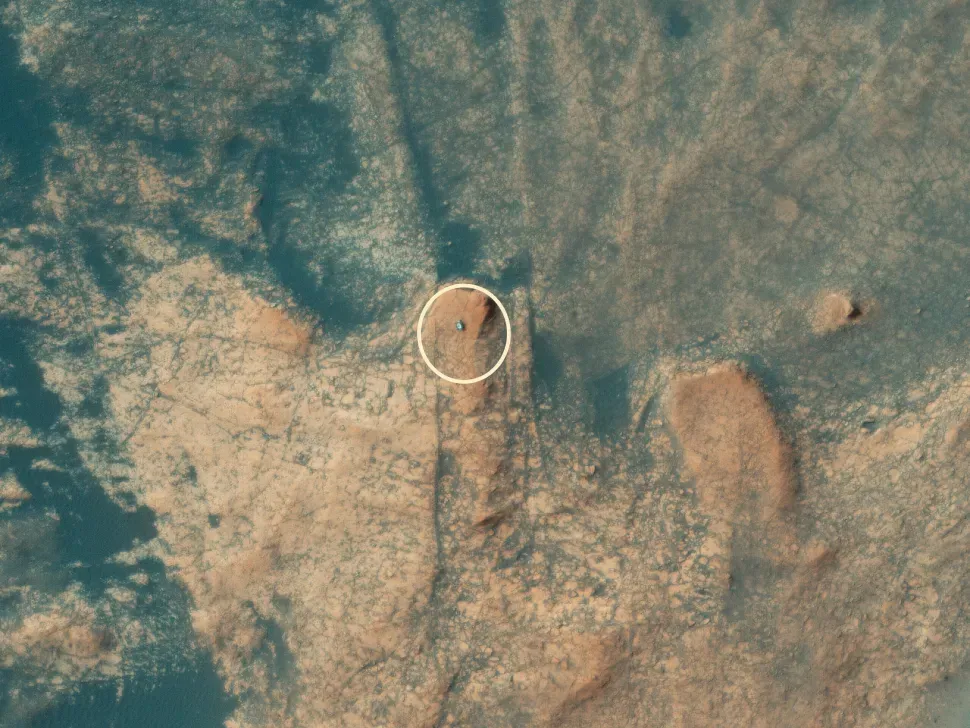

Observed from miles above by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, a metallic robot shines on the Martian surface below. In this case, the mysterious object is precisely what it appears to be: NASA’s Curiosity rover, steadily ascending Mount Sharp several years into its mission to explore Mars. While conclusive evidence of past life on the planet remains elusive, we can affirm that Mars is currently the only known planet in the universe solely inhabited by robots.